top of page
United States Constitution Review
SS.7.C.1.5
Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
Articles of Confederation: First attempt at a constitution in the colonies.
Weaknesses:
-
Gave most power to the states because the people were scared of a powerful central government.
-
The federal government had no power to collect taxes,
-
No central government or executive branch to enforce the laws,
-
No judicial branch, no Supreme court, no federal court system to hear disputes between states all states had to agree to amend the Articles.
-
Articles of Confederation led to Shays’ Rebellion – farmer’s protests against taxes demonstrate a need for a stronger central government.
Articles of Confederation were replaced by the Constitution
SS.7.C.1.6
Interpret the intentions of the Preamble of the Constitution.
Preamble’s goals:
-
Unite the 13 states with a strong central government
-
Create a fair justice system to settle disputes in the nation
-
A government that establishes a peaceful society
-
Protection of the citizens through national defense
-
To create conditions to benefit all Americans
-
The government should represent the people in order to allow for individual freedom and choice for now and the future
SS.7.C.1.7
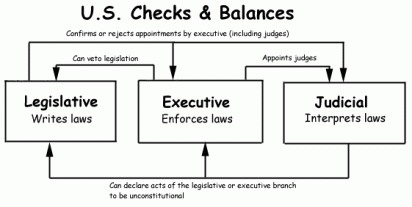
Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances.
1. Separation of Powers: Three branches have three different jobs,
2. Checks and balances: The three branches check one another to prevent one from gaining too much power
Legislative: Congress; makes laws; Article 1
Executive: President; enforces laws; Article 2
Judicial: Supreme Court; interprets laws; Article 3
SS.7.C.1.8
Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of rights.
Federalists: supported the Constitution; wanted a strong central government; Madison, Hamilton, and Jay wrote Federalists papers trying to get the public to support the Constitution.
Anti-Federalists: against the Constitution, wanted strong state governments and a weak central government and a Bill of Rights.
Here's More...
bottom of page

